We found 4603 price guide item(s) matching your search
There are 4603 lots that match your search criteria. Subscribe now to get instant access to the full price guide service.
Click here to subscribe- List
- Grid
-
4603 item(s)/page
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1924 impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND 1924, flambé ox-blood and purple glaze, stoneware 27.5cm high (10 7/8in high) Kingham & Orme 3-6 December 2020, lot 1022 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1922 impressed RUSKIN MADE IN ENGLAND 1922, ox-blood glaze, stoneware 20.5cm high (8 1/16in high) Kingham & Orme, 3-6 December 2020, lot 1029 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1910 impressed RUKSIN POTTERY 1910, flambé sang de boeuf glaze, stoneware 24.5cm high (9 5/8in high) What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY SIX GINGER JARS AND COVERS, 1913-1925 impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND and dates 1925, 1913, 1920, 1921, 1922 and 1922 respectively, lustre glazed stoneware (12) 21cm high (8 ¼in high) and smaller What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY FIVE VASES, EARLY 20TH CENTURY each with impressed factory marks, to include; a LARGE LUSTRE VASE, dated 1924, 25.3cm high (10in high); a SHOULDERED VASE, with floral decoration, dated 1906, 19.6cm high (7¾in high); a BLUE LUSTRE VASE, circa 1920, 15.7cm high (6¼in) high; a PINK LUSTRE VASE, dated 1922, 16cm high (6¼in high); a BALUSTER VASE, dated 1906, 14.5cm high (5¾in high), lustre-glazed stoneware (5) What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY THREE VASES, CIRCA 1920 each stamped with manufacturer's marks, the taller green vase stamped 1922, glazed earthenware (3) 28cm high, 24cm high and 24cm high (11in high, 9 ½in high and 9 ½in high) The taller green vase Ex-W. Howson Taylor Collection. What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED BALUSTER VASE, 1906 impressed RUSKIN POTTERY WEST SMETHWICK 1906, lavender glaze, stoneware 18cm high (7 1/16in high) What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY THREE VASES, CIRCA 1920 each with impressed marker's marks, to include; a YELLOW TWIN HANDLED VASE, 25cm high (9 ¾in high) ; a WHITE TWIN HANDLED VASE, dated 1927, 25.5cm high (10in high); a BULBOUS CRYSTALLINE GLAZED VASE, 20.4cm high (8in high), stoneware (3) What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1916 impressed RUKSIN ENGLAND 1916, ox-blood and lavender glaze, stoneware 20.3cm high (8in high) What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY VASE, 1932 impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND 1932, crystalline glaze, stoneware 14cm high (5 ½in high) William Howson Taylor Collection; Ferneyhough Collection, no. 464Victoria and Albert Museum Exhibition of Ruskin Pottery, 1975, no. 68Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery no.116Richard Dennis Collection, Kinghams, 21 June 2021, lot 21 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1906 printed RUKSIN POTTERY WEST (..obscured) 1906, streaked flambé glaze, with speckling, stoneware 18cm high (7 1/16in high) Anthony Cross Collection, Kinghams, 2021, lot 47 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1933 impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND 1933, flambé ox-blood glaze with green speckling, stoneware 21cm high (8 ¼in high) What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY BOWL AND ASSOCIATED STAND, 1920s bowl impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND 1924, stand impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND, flambé glaze, stoneware(2) bowl 11cm high, 21.8cm diameter (4 3/8in high, 8 5/8in diameter)stand 6cm high, 15.2cm diameter (2 3/8in high, 6in diameter) What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED TWIN-HANDLED VASE, 1933 impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND 1933, flambé ox-blood and lavender glaze with green speckling, stoneware 23.5cm high (9 ¼in high) Woolley & Wallis, 3 December 2014, lot 169 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1920s impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND, flambé and grey glaze, stoneware 20cm high (7 7/8in high) Anthony Cross Collection, Kinghams, 11 June 2021, lot 49 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1906 impressed RUSKIN POTTERY WEST SMETHWICK 1906, grey, deep purple and blue streaked glaze, stoneware 18.5cm high (7 ¼in high) Richard Dennis Collection, Kinghams, 2021, lot 28 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH FIRED VASE, 1933 impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND 1933, ox-blood glaze, with green speckling, stoneware 10.5cm high (4 1/8in high) Richard Dennis Collection, Kinghams, 17 April 2021, lot 23 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
RUSKIN POTTERY HIGH-FIRED VASE, 1924 impressed RUSKIN ENGLAND 1924, flambé glaze, stoneware 22cm high (8 5/8in high) Kinghams, 5 December 2020, lot 1026 What distinguishes Ruskin Pottery even today is the glazes – crystalline, lustre and sang de boeuf (or high-fired flambé). The latter was created using copper and iron oxides. Founded by Edward R. Taylor in 1898, the studio pottery was then continued by his son William Howson Taylor (1876-1935). It was located in Smethwick in Staffordshire. Historically it can be viewed as part of a revival of interest in ceramics in Europe inspired by Chinese glazes and oriental forms. Potters sought to create new glaze effects. From about 1903 William Howson Taylor developed a range of glazes in particular flambé and for the next thirty years he continued to experiment. The works he conceived can be compared to those of Chapelet, Delaherche and Dalypayrat in France. As no one glaze can be repeated each piece produced in the pottery can be regarded as unique.At its peak the pottery had twenty employees, five lustre kilns and one high-firing kiln. In 1933 the pottery closed.
Ruskin Pottery - A High Fired vase and stand, circa 1925, slender shouldered sleeve form with everted rim, Sang De Boeuf and lavender curtained glazed with green oxide speckles, impressed marks to base, height 59cm, the stand, of stepped circular form, modelled in the Chinese style, with penwork band, and geometric borders, on four feet, overall height 67cm.
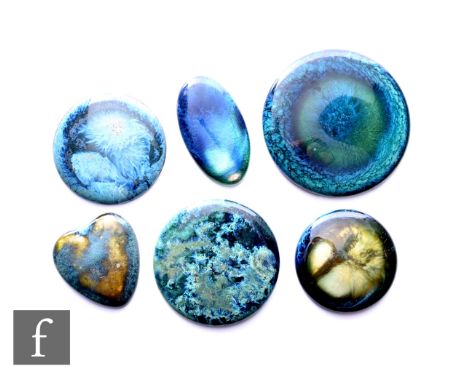
Ruskin Pottery - Three Ruskin Pottery trade postcards illustrating Crystalline Glazes, one with handwritten note to reverse 'Retail - What would you like. I had better not send that as your fittings are different, say if not so', possibly referring to the illustration of the lamp to reverse. (3)
An Edward VII Silver Napkin-Ring, by A. E. Jones, Birmingham, 1908, circular and applied with three foliage ornaments centring a Ruskin pottery cabochon, 48mm diameter, 32mm high, gross weight 1oz 1dwt, 33grProvenance: The Lion Collection.Marked near rim. The marks are clear. There is some overall surface scratching and wear, consistent with age and use.
-
4603 item(s)/page